- 16.4.1 Replication Features and Issues
- 16.4.1.1 Replication and AUTO_INCREMENT
- 16.4.1.2 Replication and Character Sets
- 16.4.1.3 Replication of CREATE ... IF NOT EXISTS Statements
- 16.4.1.4 Replication of CREATE TABLE ... SELECT Statements
- 16.4.1.5 Replication with Differing Table Definitions on Master and Slave
- 16.4.1.6 Replication and DIRECTORY Table Options
- 16.4.1.7 Replication of DROP ... IF EXISTS Statements
- 16.4.1.8 Replication of Invoked Features
- 16.4.1.9 Replication with Floating-Point Values
- 16.4.1.10 Replication and FLUSH
- 16.4.1.11 Replication and System Functions
- 16.4.1.12 Replication and LIMIT
- 16.4.1.13 Replication and LOAD DATA INFILE
- 16.4.1.14 Replication and the Slow Query Log
- 16.4.1.15 Replication During a Master Crash
- 16.4.1.16 Replication During a Master Shutdown
- 16.4.1.17 Replication and max_allowed_packet
- 16.4.1.18 Replication with MEMORY Tables
- 16.4.1.19 Replication of the System mysql Database
- 16.4.1.20 Replication and the Query Optimizer
- 16.4.1.21 Replication and Reserved Words
- 16.4.1.22 Slave Errors during Replication
- 16.4.1.23 Replication during a Slave Shutdown
- 16.4.1.24 Replication and Server SQL Mode
- 16.4.1.25 Replication and Temporary Tables
- 16.4.1.26 Replication Retries and Timeouts
- 16.4.1.27 Replication and Time Zones
- 16.4.1.28 Replication and Transactions
- 16.4.1.29 Replication and Triggers
- 16.4.1.30 Replication and TRUNCATE TABLE
- 16.4.1.31 Replication and Variables
- 16.4.1.32 Replication and Views
This section discusses the rules that are applied when a
CREATE TABLE ...
SELECT statement is replicated.
Note
CREATE TABLE ...
SELECT always performs an implicit commit
(Section 12.3.3, “Statements That Cause an Implicit Commit”).
Statement succeeds.
A successful
CREATE TABLE ...
SELECT replicates as follows:
STATEMENTorMIXEDformat. TheCREATE TABLE ... SELECTstatement is itself replicated.ROWformat. The statement is replicated as aCREATE TABLEstatement followed by a series ofbinwriteevents (that is, binary inserts).
Statement fails.
A failed CREATE
TABLE ... SELECT replicates as follows:
Statement does not use
IF NOT EXISTS. The statement has no effect. However, the implicit commit caused by the statement is logged. This is true regardless of the replication format, storage engine used, and the reason for which the statement failed.-
Statement uses
IF NOT EXISTS. The failure is handled according to the replication format. If the row-based format is in use, the action taken depends additionally on whether the table to be created uses a transactional or nontransactional storage engine, and on the reason for the failure:STATEMENTorMIXEDformat. TheCREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS ... SELECTis logged with an error.-
ROWformat. Failure of aCREATE TABLE ... SELECTthat includesIF NOT EXISTSis handled differently depending on the reason for the failure, as shown in the following table.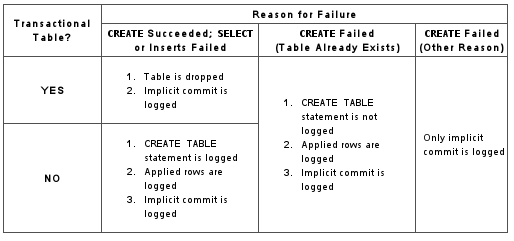

User Comments
Add your own comment.